

The structure of the tetracyclic ring of cholesterol contributes to the fluidity of the cell membrane, as the molecule is in a trans conformation making all but the side chain of cholesterol rigid and planar. The membrane remains stable and durable without being rigid, allowing animal cells to change shape and animals to move. Through the interaction with the phospholipid fatty-acid chains, cholesterol increases membrane packing, which both alters membrane fluidity and maintains membrane integrity so that animal cells do not need to build cell walls (like plants and most bacteria). The hydroxyl group of each cholesterol molecule interacts with water molecules surrounding the membrane, as do the polar heads of the membrane phospholipids and sphingolipids, while the bulky steroid and the hydrocarbon chain are embedded in the membrane, alongside the nonpolar fatty-acid chain of the other lipids. It is required to build and maintain membranes and modulates membrane fluidity over the range of physiological temperatures. Function in cells Membranes Ĭholesterol composes about 30% of all animal cell membranes. Specially designed vegetarian experimental diets have been produced yielding upwards of 700 mg/day. The intake of naturally occurring phytosterols, which encompass plant sterols and stanols, ranges between ≈200–300 mg/day depending on eating habits. When intestinal lining cells absorb phytosterols, in place of cholesterol, they usually excrete the phytosterol molecules back into the GI tract, an important protective mechanism. In larger quantities they produce phytosterols, chemically similar substances which can compete with cholesterol for reabsorption in the intestinal tract, thus potentially reducing cholesterol reabsorption. Plants make cholesterol in very small amounts. However, during the first seven hours after ingestion of cholesterol, as absorbed fats are being distributed around the body within extracellular water by the various lipoproteins (which transport all fats in the water outside cells), the concentrations increase. For these reasons, cholesterol in food, seven to ten hours after ingestion, has little, if any effect on concentrations of cholesterol in the blood.
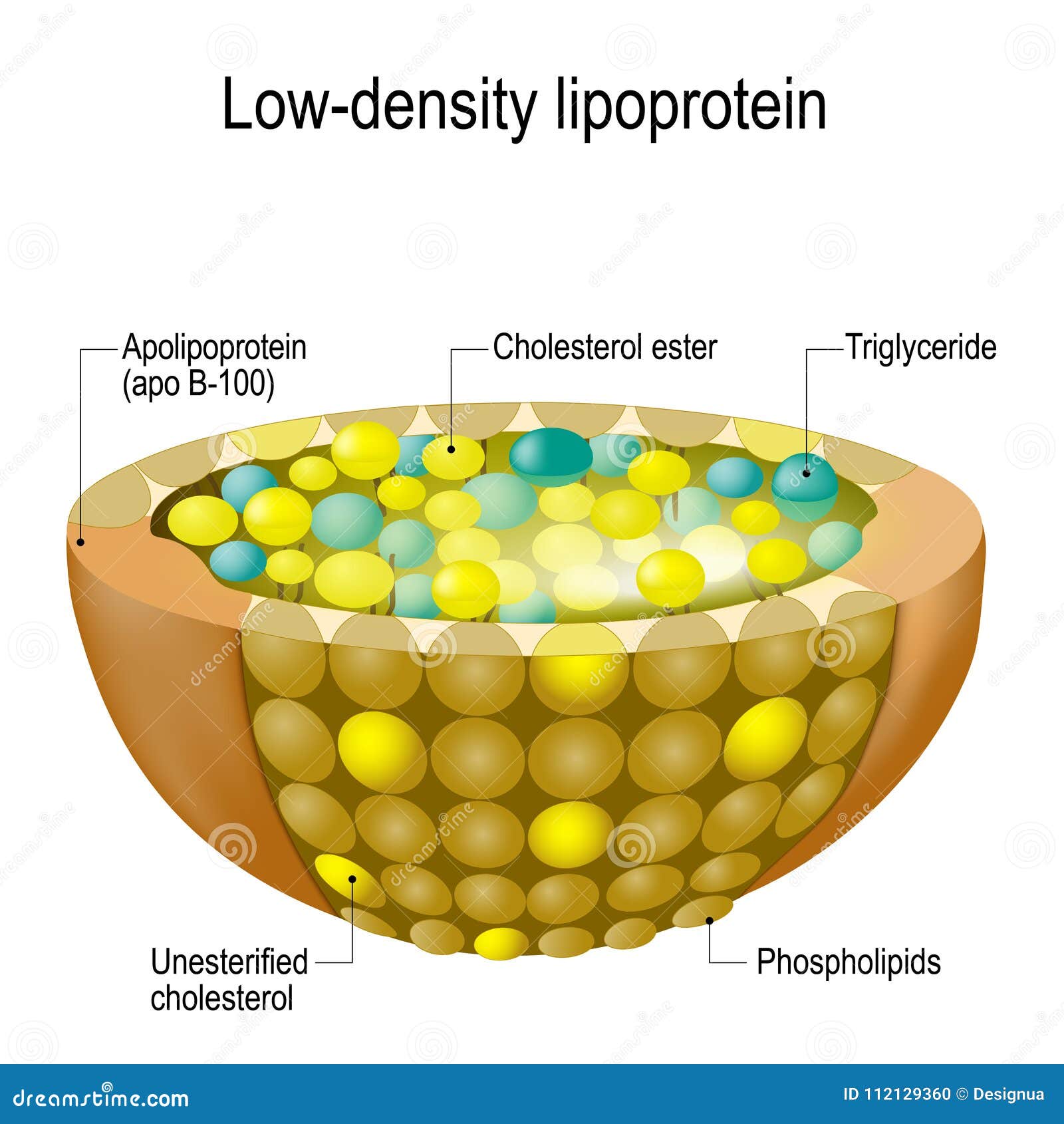
The body also compensates for absorption of ingested cholesterol by reducing its own cholesterol synthesis. Most ingested cholesterol is esterified, which causes it to be poorly absorbed by the gut. Typical daily cholesterol dietary intake for a man in the United States is 307 mg. This is followed by 19 additional steps to convert the resulting lanosterol into cholesterol.Ī human male weighing 68 kg (150 lb) normally synthesizes about 1 gram (1,000 mg) of cholesterol per day, and his body contains about 35 g, mostly contained within the cell membranes. This begins with the mevalonate or HMG-CoA reductase pathway, the target of statin drugs, which encompasses the first 18 steps. The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek chole- ( bile) and stereos (solid), followed by the chemical suffix -ol for an alcohol.Ĭholesterol is essential for all animal life, with each cell capable of synthesizing it by way of a complex 37-step process. 4.1 Medical guidelines and recommendations.3.4 Metabolism, recycling and excretion.3.3 Plasma transport and regulation of absorption.3.2 Regulation of cholesterol synthesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
